-
Tetrathiafulvalene-1,3,5-triazines as (Multi)Donor-Acceptor Systems with Tunable Charge Transfer: Structural, Photophysical, and Theoretical Investigations

F. Pop, F. Riobé, S. Seifert, T. Cauchy, J. Ding, N. Dupont, A. Hauser, M. Koch and N. Avarvari
Inorganic Chemistry, 52 (9) (2013), p5023-5034


DOI:10.1021/ic3027336 | unige:27865 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
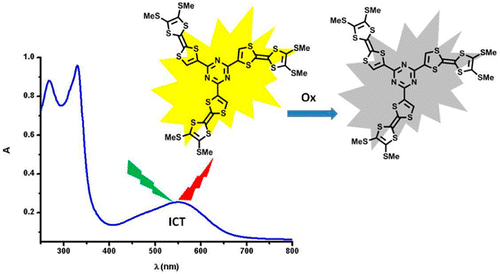
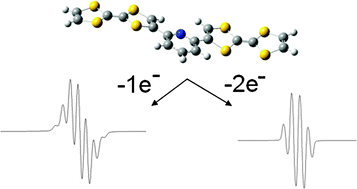
Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions between chlorinated 1,3,5-triazines (TZ) and tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) trimethyltin derivatives afford mono- and C3 symmetric tris(TTF)-triazines as donor–acceptor compounds in which the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) is modulated by the substitution scheme on TTF and TZ and by chemical or electrochemical oxidation. The TTF-TZ-Cl2 and (SMe)2TTF-TZ-Cl2 derivatives show fully planar structures in the solid state as a consequence of the conjugation between the two units. Electrochemical and photophysical investigations, supported by theoretical calculations, clearly demonstrate that the lowest excited state can be ascribed to the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) π(TTF)→π*(TZ) transition. The tris(TTF) compound [(SMe)2TTF]3-TZ shows fluorescence when excited in the ICT band, and the emission is quenched upon oxidation. The radical cations TTF+• are easily observed in all of the cases through chemical and electrochemical oxidation by steady-state absorption experiments. In the case of [(SMe)2TTF]3-TZ, a low energy band at 5000 cm–1, corresponding to a coupling between TTF+• and TTF units, is observed. A crystalline radical cation salt with the TTF-TZ-Cl2 donor and PF6– anion, prepared by electrocrystallization, is described.